Weather radar, Weather Monitoring Systems (WMS), and Automated Weather Stations (AWS) are distinct in terms of their functionality, data collection methods, and applications. Here’s a breakdown of the key differentiating factors between these weather monitoring technologies:
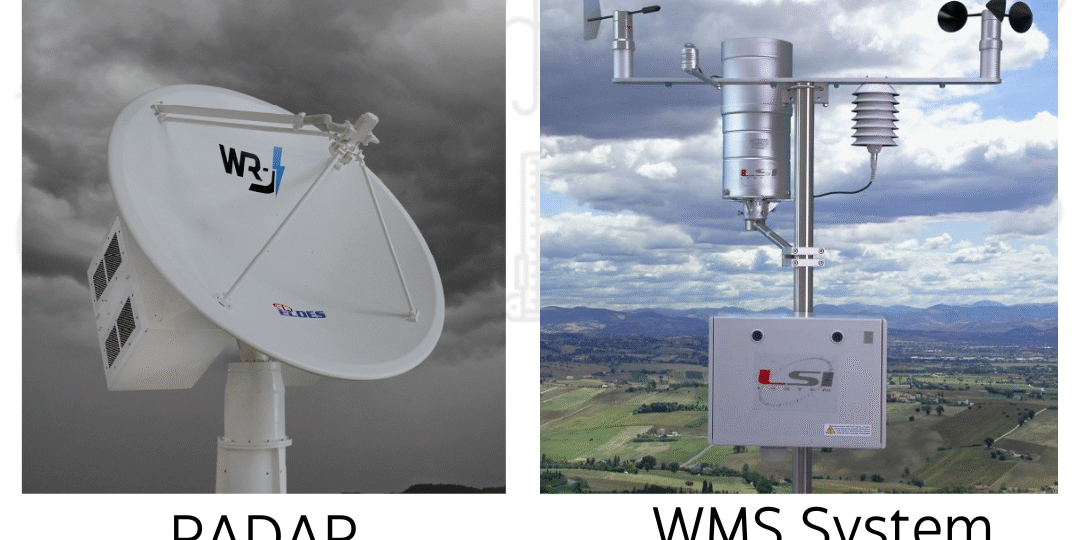
Weather Radar:
- Purpose: Weather radar is primarily used for detecting and tracking precipitation, including rain, snow, hail, and storms. It provides information about the location, intensity, and movement of precipitation systems.
- Coverage: Weather radar has a wide coverage area, typically spanning several hundred kilometers. It can monitor weather conditions over a large geographical region, making it suitable for regional and national-scale observations.
- Data Collection: Radar systems emit radio waves and measure the reflected signals to determine the presence and characteristics of precipitation. They use sophisticated technology, such as Doppler radar, to detect motion and velocity of precipitation particles.
- Applications: Weather radar is essential for short-term weather forecasting, monitoring severe weather events, issuing warnings, and studying precipitation patterns. It is particularly valuable for identifying and tracking storms, thunderstorms, tornadoes, and hurricanes.

Weather Monitoring Systems (WMS):
- Purpose: WMS are designed to collect and monitor various weather parameters, such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, wind direction, atmospheric pressure, and solar radiation. They provide localized observations for weather monitoring.
- Coverage: WMS typically cover a smaller area, ranging from a few meters to a few kilometers. They are often deployed in specific locations, such as airports, research stations, or urban areas, to gather detailed weather data.
- Data Collection: WMS employ sensors and instruments to measure weather variables at the ground level. They can include instruments like thermometers, barometers, anemometers, pyranometers, and rain gauges.
- Applications: WMS are used for various applications, including agriculture, aviation, environmental monitoring, urban planning, and research. They provide on-site weather data for localized weather forecasting, climate studies, and specific industry requirements.
Automated Weather Stations (AWS):
- Purpose: AWS are a subset of WMS that are fully automated and operate without human intervention. They are designed to collect and transmit weather data continuously and autonomously.
- Coverage: Similar to WMS, AWS cover a relatively smaller area and are typically installed at specific locations. They can be deployed in remote or inaccessible areas where continuous weather monitoring is required.
- Data Collection: AWS consist of sensors and instruments that measure weather variables, similar to WMS. They are equipped with data loggers and communication systems to transmit the collected data to a central location.
- Applications: AWS are used in various fields, including agriculture, hydrology, research, and aviation. They provide real-time weather data for local forecasting, climate monitoring, water resource management, and other specific applications.
In summary, weather radar is specialized in detecting and tracking precipitation on a regional scale, while WMS and AWS focus on collecting a broader range of weather parameters at specific locations. Each technology serves unique purposes and plays a crucial role in weather monitoring, forecasting, and research.